Company inside only IPV6 address can group local area network? Can I use the Internet normally?
Good evening, students!
Today we are going to talk about whether IPv6 addresses can only be used in local area networks , and how to set up and assign IPv6 addresses .
In the daily network environment, we are probably most familiar with IPv4 addresses, and many local networks are even "IPv4 main, IPv6 auxiliary" combination mode。But have you ever wondered if it would be possible to build a functioning local area network without IPv4 at all and only with IPv6?The answer is: yes!
For more information, please scan the WhatsApp QR code below to contact customer service.

01 Introduction to IPv6
IPv6 address length up to 128 bits, support more terminal Internet access.
IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6) is the successor to IPv4 and uses a 128-bit address format that provides nearly unlimited address space for the entire world。A typical IPv6 address looks like this:
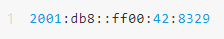
Compared to the 32-bit address of IPv4 ( such as 192.168.1.1 ) , IPv6 not only solves the problem of address exhaustion , but also optimizes routing efficiency , supports automatic configuration , and has a more perfect security mechanism .
Is it possible to use IPv6 only for local networks?
Of course IPv6 has a complete network communication capability, which is enough to support a complete local area network to achieve device intercommunication, resource sharing and access to the Internet (provided that the export supportsIPv6) 。
In IPv6-only local networks, the following functions can still be used:
· Device interoperability ( Ping , SSH , RDP , etc . )
· Local DNS resolution ( AAAA record support required )
· File sharing, print services
· Intranet access servers / databases
· Visit websites that support IPv6 ( if the outgoing network supports it )
02 How to allocate IPv6 addresses in a local network?
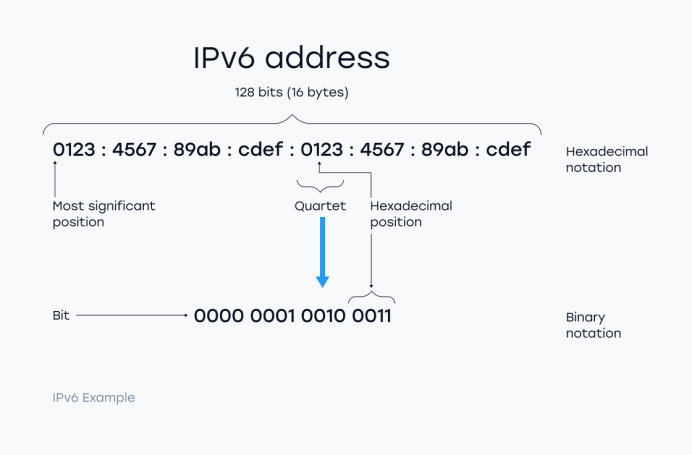
IPv6 no longer uses the traditional " subnet mask , " but instead uses the prefix length for partitioning , such as /64。
IPv6 address allocation methods are mainly the following:
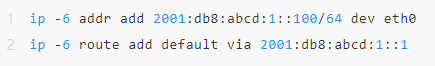
1. Static allocation ( Manual Configuration )
Administrators manually specify IPv6 addresses, prefixes, and gateways for each device, ideal for small networks or fixed server devices.
Example configuration ( Linux ) :
2. SLAAC (Stateless Address Auto-Configuration (SLAAC)
The device obtains the prefix ( NDP ) automatically from the local router and generates the host part based on the MAC address .
Just enableRA (Router Advertisement) ,The terminal device can automatically generate an available IPv6 address.
3. DHCPv6 (Stateful Address Allocation)
By DHCPv6 Server centralized allocation of addresses, suitable for enterprise network, easy to unified management and audit.
03 IPv6 Address Structure
The IPv6 address consists of a network prefix + interface identifier.
IPv6 addresses are generally divided into two parts:
Prefix ( Prefix ) : such as 2001 : db8 : abcd : 1 :: / 64 , represents the subnet ; Interface identifier ( Interface ID ) : such as :: 100 , represents the specific identifier of the device , can be generated by MAC address ( EUI-64 ) or randomly generated

Example of a typical setup for a full IPv6 local network
function | Introductions |
Address allocation | SLAAC or DHCPv6 (/ 64 prefix) |
Router Support | RA broadcast prefix must be supported |
DNS support | Using IPv6 AAAA records |
Local communication | Using Link-Local or Global Addresses |
Export visits | The router needs to support IPv6 export, such as NAT64 / DNS64 or IPv6 direct connection |
How is the daily usage experience?
If your network environment ( e.g. educational network , operator 's export ) supports IPv6 natively , you will find that :
· IPv6 network has stable speed and low latency;
· More and more websites support IPv6 access (e.g。Google、Facebook、YouTube) ;
· The internal network equipment configuration is more automatic, no NAT, and communication efficiency is higher.
However, note that:
· Some old equipment and software do not support IPv6 well;
· Some network applications ( such as some remote desktop clients ) depend on IPv4 by default ;
· Access may be restricted if IPv6 is not turned on on on the exit network.
FAQs
Q: Do you still need a submask in IPv6?
A : IPv6 uses a prefix length ( such as / 64 ) instead of a traditional subnet mask .
Q: Can IPv6 address still be broadcast?
A : IPv6 does not support broadcast , use multicast ( Multicast ) mechanism to replace , more efficient .
Q: Can multiple IPv6 addresses be assigned to one interface?
A: Yes. A network card interface can have multiple IPv6 addresses, including global address, link-local address, temporary address, etc.
We shared this today. Goodbye next time!


