Is there any difference between HTTP and HTTPS other than encryption and non-encryption?
Good evening, my friends!
When we go online, we often see websites with "http" or "https" in front of them. They all represent hypertext transfer protocols. (HyperText Transfer Protocol) But there's one key difference between the two, and that's security. Today, we will delve into the differences between HTTPS and HTTP, as well as how they work and use cases.
If you want to get more information, scan the QR code below to contact customer service.

01 Basic definitions of HTTP and HTTPS
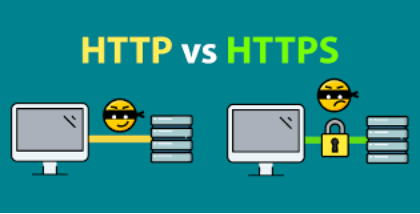
HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) is one of the most common protocols we use when surfing the Internet. Almost all web browsers use the HTTP protocol to request and receive web content。The way it works is that the browser sends a request to the server, and the server returns the corresponding data (such as web pages, images, etc.) 。However, the HTTP protocol itself is plain text transmission, which means that any data transmitted over the network can be intercepted by man-in-the-middle.
HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure) is the "secure version" of HTTP。It is based on the HTTP protocol and combines the SSL / TLS encryption protocol so that the content of the communication is encrypted. This means that even if someone intercepts data in the network, they won't be able to read its contents.Thus, HTTPS provides not only data transfer but also authentication and encryption protection.
02 How HTTP and HTTPS work
1. How HTTP works
The working process of the HTTP protocol is relatively simple.The client (browser) sends a request to the server, and the server returns the contents of the request.Since the HTTP protocol does not have an encryption mechanism, all data is transmitted as plain text, which also poses a security risk.For example, hackers can intercept and tamper with data through man-in-the-middle attacks.
2. How HTTPS works
The work of the HTTPS protocol is relatively complex, but the basic steps are as follows:
1.SSL / TLS handshake process: When the client (browser) requests an HTTPS website, a series of encryption and authentication processes are carried out between the client and the server。First, the browser exchanges certificates with the server to ensure that the server's identity is authentic.The data is then encrypted and decrypted using public and private keys.
2 . Data Encryption : Once a secure connection is established , all data transmitted is protected using encryption algorithms . Even if hackers are able to intercept the data , they are unable to read the content .
3. Data integrity verification: The HTTPS protocol also verifies whether the data has been tampered with during transmission。If the data is modified during transmission, the communication is broken, thus preventing tampering.
03 Main differences between HTTP and HTTPS
Characteristic |
Safety |
interface |
certificate |
performance |
use |
04 Advantages and Necessity of HTTPS
1. Data encryption and privacy protection
The most significant advantage of HTTPS is data encryption。Privacy protection is becoming more and more important in modern networks, especially when dealing with personal sensitive information (such as user names, passwords, payment information, etc.) at the same time。HTTPS ensures that even if the data is intercepted in the process of transmission, the hacker cannot decrypt and obtain the information.
2. Prevent middleman attacks
Man-in-the-middle attack (MITM) is a common way of network attack, attackers can hijack the communication between users and servers, tamper with or steal data。HTTPS can effectively prevent such attacks by using SSL / TLS certificates to verify the identity of the server and ensure that the user is connected to the correct server.
3. Improve search engine rankings
In recent years, search engines such as Google have begun to incorporate HTTPS as a component of their rankings. Websites that use HTTPS are usually shown first in search results, which has a positive effect on the website's SEO optimization.
4. Enhancing user trust
When a browser visits an HTTPS site, it usually displays a small lock icon in the address bar or marks it as "safe." This gives users more trust in the site, especially when making payments or submitting personal information. If the site does not have HTTPS, the browser may display a "unsafe" warning, which will create concerns and affect the user experience and trust of the site.
In our real life, most of the websites we visit are HTTPS. It is very rare to use HTTP for access. When we do our experiments, we use HTTP, but in real life, we use HTTPS more.
Because the network contains a large number of our identity information and personal data, encrypted through HTTPS, you can avoid information being tampered with or stolen by hackers.
05 How to Enable HTTPS
1. Obtaining an SSL / TLS certificate: First, you need to purchase and install an SSL / TLS certificate。There are a number of providers that offer certificates, such as Let's Encrypt, which offers free SSL certificates for personal websites or small businesses.
2. Configuring the web server: Depending on the web server you are using (e.g. Apache, Nginx, IIS, etc.) , you will need to configure the server to support HTTPS。This usually requires you to specify an SSL certificate for the server and enable the SSL / TLS protocol in the configuration file.
3. Mandatory HTTPS: redirect HTTP (301 redirect) , make sure all HTTP requests are automatically forwarded to HTTPS。In this way, users will be able to access the website through a secure connection regardless of how they enter the URL.
Hopefully this article will help you better understand the difference between HTTP and HTTPS, and how HTTPS plays a role in protecting digital security and user privacy in the modern web environment.
For more http resources, follow the Facebook account&youtube account: Thinkmo Dumps


