Hey! Guys,
it's been a long time since we talked about Huawei devices.
Although the network equipment market is now full of various players, and manufacturers like Cisco, Ruijie, and H3C all have their own strengths, Huawei's momentum in the domestic market is quite strong.
Whether it's the switches in enterprise parks or the core routers of operators, Huawei devices can be seen everywhere. In the network architectures of many state - owned enterprises and large companies, Huawei devices are the main force. Therefore, if you want to thrive in the domestic network engineer community, mastering Huawei commands is a basic skill.
For more information, please scan the WhatsApp QR code below to contact customer service.

![]() ?
?
The question mark command is like a universal dictionary with extremely flexible usage.
When you don't know what command to enter, just type a "?", and all available commands will be listed for you. When you can't remember what parameters should follow a command, add a "?" after the command, and the next - level parameters will be displayed immediately.
For example, when you enter "display ip?", the device will tell you what parameters can be filled in next. If no additional parameters are needed, "<Enter>" will be displayed.
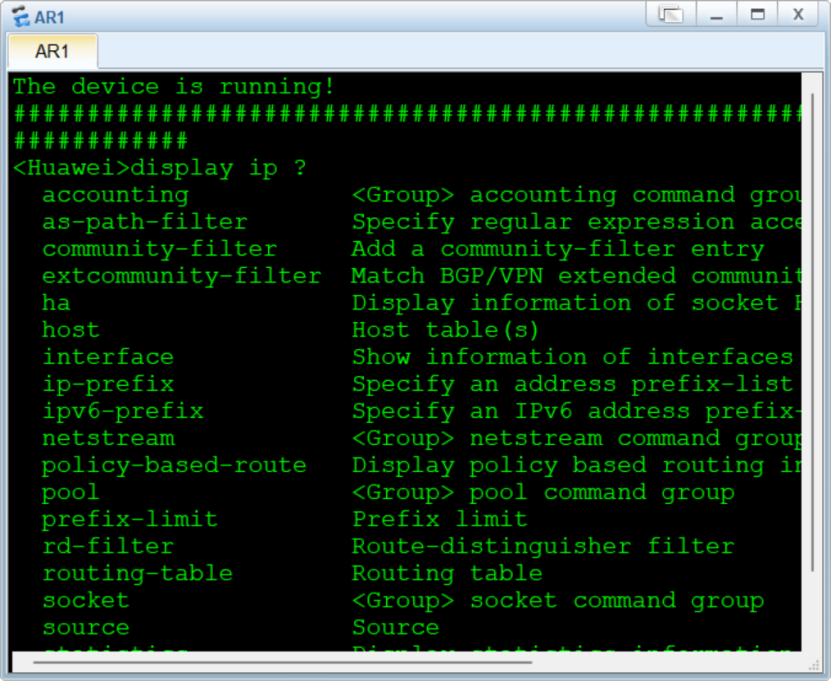
![]() debugging
debugging
This command must be used with specific options. Entering it alone won't work. It can output detailed debugging information of a certain application, protocol, or service. For example, if you want to monitor changes in the routing table, enter "debugging ip routing", and there will be a record every time a route is added or removed.
Note: Although the debugging function is useful, its process priority is particularly high, which may affect device performance. Don't turn it on casually unless necessary.
![]() display interface
display interface
Want to know the interface status? This command is definitely right. It can display a bunch of key information:
The physical status of the interface (up/down), the protocol status of the interface, bandwidth utilization, error packet statistics, MTU value.
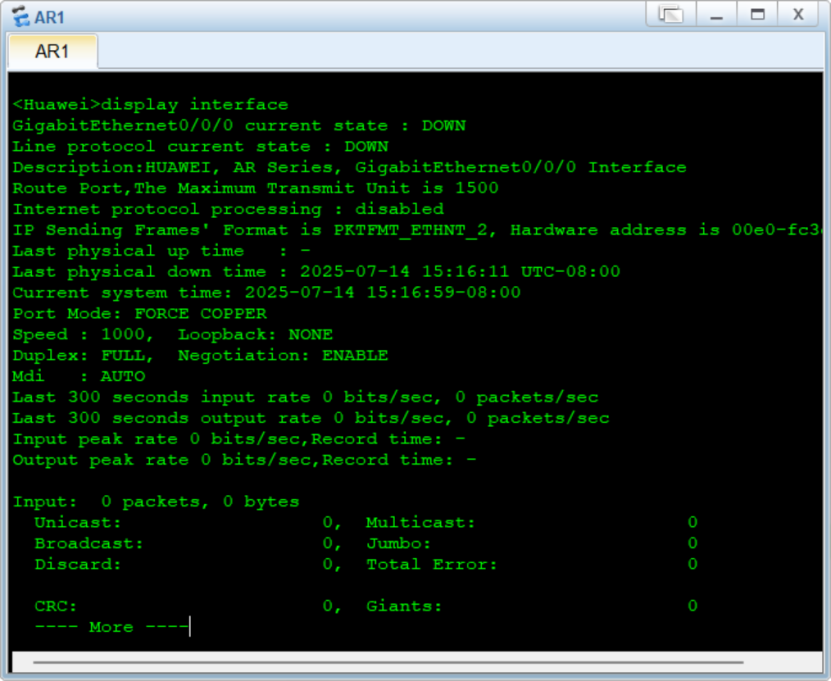
Troubleshooting interface failures relies entirely on it. You can also specify a specific interface, such as "display interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1".
![]() undo shutdown
undo shutdown
This command is used to activate the interface and should be used in the interface view. It may be used when a new interface has just been configured or when there is a problem with the interface. Sometimes, when the interface status is incorrect, first enter "shutdown" to close it, and then enter "undo shutdown" to reactivate it. Maybe it will work. This command can also be abbreviated as "undo shut".
![]() display version
display version
Entering this command allows you to view a bunch of basic information about the device: system version, device model, startup time, memory size, flash capacity, and the status of the configuration register.
When you want to view the basic information of the device during daily inspections, entering this command is definitely correct, and it can also be abbreviated as "display ver".
![]() display ip interface brief
display ip interface brief
This command is a shortcut for viewing interface IP information. The output is concise and clear: interface name, IP address, physical status, and protocol status. You can see the key information of all interfaces at a glance.
It has much less redundant content compared to "display ip interface". It is the most convenient to use when quickly checking the interface status in daily use.
![]() display ip routing-table
display ip routing-table
Want to view the routing table? Use this command. All the information such as all the networks that the device can access, the routing type, the metric value, and the next hop is included in it.
You can also view a specific type of route alone. For example, "display ip routing-table protocol ospf" will only display OSPF routes.
![]() system-view、user-interface、interface
system-view、user-interface、interface
Huawei devices have different operation views, and what can be done in each view is different. To configure the device proficiently, one has to understand how to switch between these views.
When you first log in to the device, you are in the user view (the prompt is >), and by entering "system-view", you can enter the system view (the prompt becomes [Huawei]), and only then can you modify the configuration.
If you want to set the login interface, enter "user-interface" from the system view to enter the user interface view.
To modify the interface parameters (such as configuring the IP), enter "interface" followed by the interface name to enter the interface view
[Huawei-GigabitEthernet0/0/1].
![]() display current-configuration
display current-configuration
This command can display all the configurations currently running on the device. It's an absolute daily essential for network engineers.
Want to see what configurations are currently set on the device? Or if there are any redundant configurations? Entering "display current-configuration" is definitely the right choice. Usually, it is abbreviated as "display cu", and this abbreviation must be remembered well.
For more Huawei Network Debug Commands resources, follow the Facebook account & youtube account: Thinkmo Dumps


