How to Isolate Multi-Tenant Networks? A Comprehensive Guide to the Core Technology of VPN Instances (VRF)
Good evening, my friends!
In modern networking environments, VPN instances (Virtual Routing and Forwarding, VRF) are a crucial networking technology.
They help isolate different network traffic on the same physical device, enhancing both security and scalability.
In enterprise networks—especially in complex branch setups or multi-tenant environments—VRF is widely applied.
If you want to get more information, scan the QR code below to contact customer service.

1. Definition
VPN Instance (VRF) is a virtual routing concept that allows the creation of multiple independent routing tables on a single physical router.
Each routing table corresponds to a virtual "VPN" ,enabling complete traffic isolation. This ensures that even when multiple users or
networks share the same physical device, their network traffic and routing information remain completely segregated without interfering with each other.
In simple terms, a VPN Instance uses virtualization technology to simulate multiple independent network environments on one physical device.
Within each environment, network traffic and configurations operate in complete isolation - essentially providing each user or department with
their own "private network space."
2.Working Principle
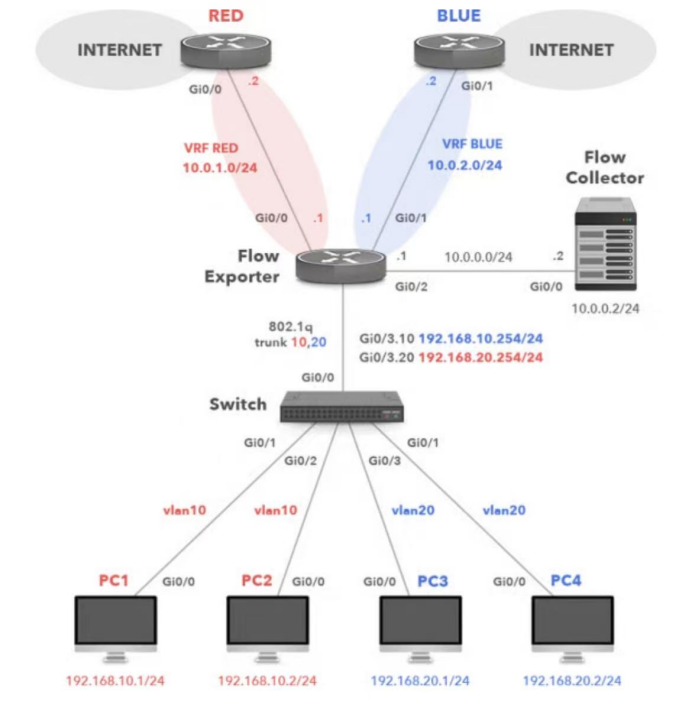
The VPN Instance (VRF) operates by configuring multiple virtual routing tables on a single physical device to achieve traffic isolation between
different networks. For example, when an enterprise has multiple branch offices or departments, a dedicated VPN Instance (VRF) can be
created for each branch or department. This ensures their routing tables remain completely independent and will not interfere with one another.
The specific workflow is as follows:
When user traffic enters the router, the router selects the corresponding virtual routing table based on traffic identifiers (such as VPN instance labels).
Each VPN instance maintains its own independent routing table, subnet, and routing decisions, ensuring traffic cannot communicate between different
instances—thereby preserving network security and privacy.
During packet forwarding, the router uses the VPN instance information to select the appropriate routing table for traffic transmission.
This mechanism essentially virtualizes multiple independent "mini-routers" within a single physical router, where the networks inside
each virtual router remain completely isolated from one another.
3.Application Scenarios
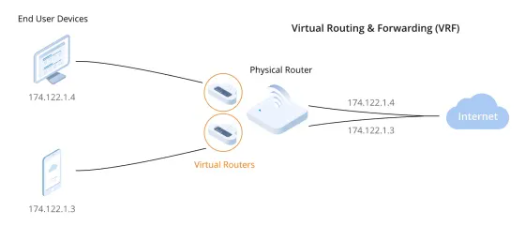
Enterprise Branch Isolation:
In large enterprises, particularly those with multiple branch offices, each branch has its own independent network requirements.
Without VPN instances, each branch would require dedicated routers or complex switching equipment, resulting in high costs
and management complexity. By implementing VRF, enterprises can create multiple isolated virtual routing environments on
a single device, achieving network segregation between branches while reducing hardware costs and simplifying administration.
Multi-Tenant Environments:
For service providers or hosted data centers, VRF technology proves extremely valuable. It enables the provisioning of isolated
network environments for different tenants on the same physical device, where each tenant's data traffic is processed independently
without interference. This allows service providers to deliver network services to multiple customers more efficiently.
Network Isolation in Virtualized Environments:
In cloud computing or data center virtualization scenarios, multiple virtual machines require segregated network environments to
ensure security. Through VPN instances, network administrators can assign distinct routing tables to different VMs, guaranteeing
that each VM's network traffic remains inaccessible to others, thereby enhancing overall security.
4. Key Configuration Considerations
Creating a VPN Instance (VRF)
When configuring a VPN instance, the first step is to define a VRF instance by assigning a unique name to identify the VPN.
For example:Create a VPN instance named "HR_VPN" Subsequently, you can configure an independent routing table and
network interfaces for this instance.

Binding Interfaces to VPN Instances
After creating a VPN instance, you need to bind physical or virtual interfaces to that specific instance. Once bound, these
interfaces will only participate in the routing table operations of their assigned VRF instance, ensuring complete traffic isolation.

Configuring Routing Protocols for VPN Instances
Each VPN instance maintains its own independent routing protocols. Typically, we configure dedicated OSPF, BGP, or other
routing protocols for each VPN instance. This ensures complete isolation of routing information between different VPN instances,
effectively preventing potential data leaks.
![]()
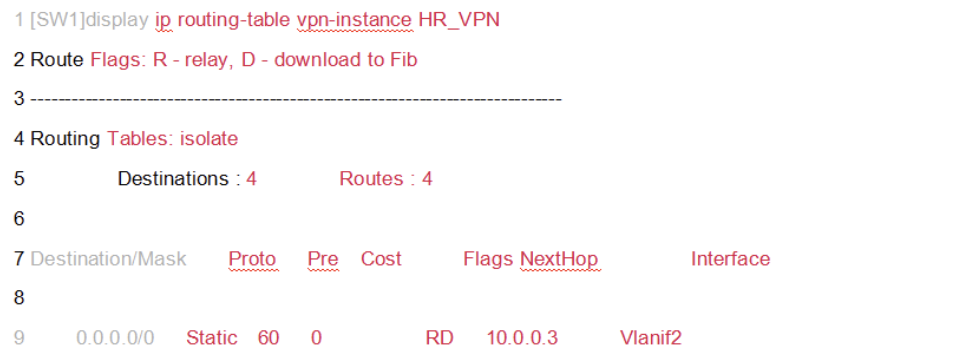
Route Isolation
After configuring VPN instances, each instance maintains a completely independent routing table.
5. Summary
VPN Instance (VRF) Overview
VPN Instance (VRF) technology enables the creation of multiple virtual routing tables on a single physical device, effectively isolating
different network traffic streams. This solution is widely implemented in three key scenarios:
For more networking resources, follow the Facebook account&youtube account: Thinkmo Dumps


